High-resolution functional connectivity
SUMMARY
Lead
Elizabeth Rizor
PIs
Scott T. Grafton, Mark Floyd Lew
Subjects
21 healthy subjects, age 21 to 36
Data type
resting fMRI
Institution
USC
Ultra-high field data for cortico-subcortical network mapping in healthy controls
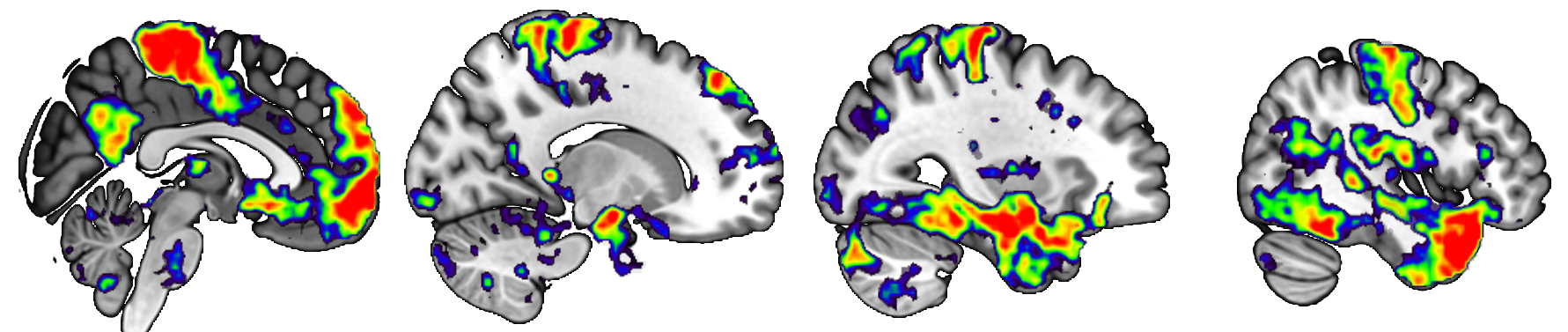
This repository consists of ultra-high field (7T), multi-echo functional connectivity (FC) data in 21 young, healthy adults. FC data acquired via fMRI are highly susceptible to influence from non-BOLD signals, such as physiological noise, head motion, and scanner effects (Buckner et al., 2013). Concerns about non-BOLD artifact have led to the increased usage of multi-echo imaging, which can be uniquely denoised with ME-ICA methods (Kundu et al., 2013). Additionally, ultra-high field imaging provides benefits over common 3T imaging by allowing for both greater image resolution and increased reliability of FC network results (Nemani & Lowe, 2021). The combination of multi-echo and ultra-high field imaging is ideal for mapping network properties of small, deep subcortical nuclei, such as those in the basal ganglia (Puckett et al., 2018).
References
Buckner, R. L., Krienen, F. M., & Yeo, B. T. T. (2013). Opportunities and limitations of intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Nature Neuroscience, 16(7), Article 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3423
Kundu, P., Brenowitz, N. D., Voon, V., Worbe, Y., Vértes, P. E., Inati, S. J., Saad, Z. S., Bandettini, P. A., & Bullmore, E. T. (2013). Integrated strategy for improving functional connectivity mapping using multiecho fMRI. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(40), 16187–16192. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1301725110
Nemani, A., & Lowe, M. J. (2021). Seed-based test–retest reliability of resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging at 3T and 7T. Medical Physics, 48(10), 5756–5764. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.15210
Puckett, A. M., Bollmann, S., Poser, B. A., Palmer, J., Barth, M., & Cunnington, R. (2018). Using multi-echo simultaneous multi-slice (SMS) EPI to improve functional MRI of the subcortical nuclei of the basal ganglia at ultra-high field (7T). NeuroImage, 172, 886–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.12.005
Publications
